In today’s rapidly advancing technological world, we are constantly upgrading our devices—new smartphones, laptops, and gadgets emerge every year, leaving our old electronics obsolete. This cycle of continuous upgrades contributes to a growing global issue: electronic waste, or e-waste. The sheer volume of discarded electronic devices is staggering, and the environmental and health risks posed by improper disposal of e-waste are significant.
However, with every challenge comes an opportunity. The e-waste crisis presents an urgent need to rethink how we dispose of old electronics, and by doing so, we can unlock valuable resources, protect the environment, and create economic opportunities. In this brief, we will explore the challenges posed by e-waste, its environmental and health impacts, and how it can be turned into an opportunity for a greener, more sustainable future.
Understanding the E-Waste Challenge
E-waste refers to discarded electronic devices such as computers, smartphones, televisions, refrigerators, and other appliances. These devices contain various materials, including metals, plastics, and hazardous substances like lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can be harmful if not properly managed. As technology evolves at an unprecedented pace, the global production of e-waste has skyrocketed.
According to the Global E-Waste Monitor, the world generated over 53.6 million metric tons of e-waste in 2019, and this number is expected to increase to 74.7 million tons by 2030. Unfortunately, only about 17.4% of global e-waste is properly collected, recycled, or reused, leaving the majority to be dumped in landfills or incinerated, leading to severe environmental and health consequences.
Visit for more details:
Environmental and Health Impacts of E-Waste
When e-waste is improperly disposed of, its harmful components can cause long-term damage to the environment and human health. The risks include:
- Soil and Water Contamination: Electronics contain hazardous substances such as lead, mercury, and arsenic. When these materials end up in landfills, they can leach into the soil and water systems, contaminating the surrounding ecosystems. This contamination can affect plant life, animal species, and ultimately human communities that rely on these natural resources.
- Air Pollution: Many e-waste disposal processes, especially in developing countries, involve burning electronics to recover metals like copper. This practice releases toxic fumes into the atmosphere, contributing to air pollution and respiratory problems for those who work in or live near informal recycling operations.
- Health Risks: The workers who handle e-waste, particularly in unregulated environments, are exposed to hazardous chemicals without adequate safety precautions. This exposure can lead to a range of health problems, including respiratory issues, neurological damage, and an increased risk of cancers.
- Resource Depletion: Electronics contain valuable materials such as gold, silver, copper, and rare earth elements. When e-waste is discarded rather than recycled, these materials are lost, increasing the demand for mining and extraction of raw materials. Mining operations, especially in developing countries, are associated with deforestation, water pollution, and displacement of local communities.

Turning E-Waste into Opportunity
The good news is that e-waste doesn’t have to be just an environmental burden. With the right strategies and technologies, we can transform the challenge of e-waste into a valuable opportunity. Here’s how:
1. Recycling Valuable Materials
One of the most effective ways to reduce the negative impact of e-waste is through recycling. Electronic devices contain valuable components such as gold, silver, platinum, copper, and rare earth metals, which can be recovered and reused. Recycling e-waste reduces the need for mining new materials, conserves natural resources, and decreases the energy required for manufacturing new devices.
For example, just one ton of old mobile phones can yield up to 300 grams of gold, 1 kilogram of silver, and 100 kilograms of copper. By efficiently extracting these materials from discarded electronics, we can create a circular economy where resources are reused instead of wasted.
2. Extending the Lifespan of Electronics
Another key opportunity lies in extending the lifespan of electronic devices. Many of the electronics we discard are still functional or can be easily repaired. Repairing, refurbishing, or upgrading devices instead of replacing them can reduce the volume of e-waste generated.
This approach also offers opportunities for businesses to tap into the growing demand for refurbished electronics. Refurbished smartphones, laptops, and other gadgets are often sold at a lower price, making technology more accessible to consumers while reducing e-waste.
3. Innovating in E-Waste Management
Innovation in e-waste management presents significant opportunities for entrepreneurs and companies that develop new technologies for recycling and disposal. Advanced recycling technologies can improve the efficiency of material recovery from e-waste and reduce the environmental impact of traditional disposal methods.
For instance, innovations in urban mining, where precious metals are extracted from e-waste using environmentally friendly processes, offer an alternative to traditional mining. Companies that invest in clean technology solutions for recycling and repurposing e-waste materials stand to benefit from the growing market for sustainable products and services.
4. Job Creation and Economic Growth
The e-waste challenge can also be an engine for job creation and economic development. By investing in e-waste recycling facilities and promoting policies that encourage responsible disposal, countries can create new industries and jobs in the waste management and recycling sectors.
According to the United Nations, for every 1,000 tons of e-waste recycled, nearly 200 full-time jobs can be created in collection, transportation, dismantling, and material recovery. This represents a significant opportunity for developing economies to build a green economy and foster sustainable growth.
5. Raising Awareness and Promoting Responsible Consumer Behavior
Consumers play a critical role in addressing the e-waste challenge. By making informed choices about how we use and dispose of electronics, we can reduce the environmental impact of our tech consumption. Raising awareness about the dangers of e-waste and the importance of responsible disposal is crucial for encouraging behavior change.
Consumers can contribute by:
- Donating or selling old electronics that are still functional.
- Participating in take-back programs offered by manufacturers and retailers.
- Supporting companies that prioritize sustainability in their products and operations.
- Choosing refurbished electronics when possible, reducing the demand for new devices.
Call Now:
Government and Corporate Responsibility
While consumers have a role to play, governments and corporations bear a significant responsibility in addressing the e-waste crisis. Policies and regulations that enforce responsible e-waste disposal, promote recycling, and incentivize sustainable product design are essential for systemic change.
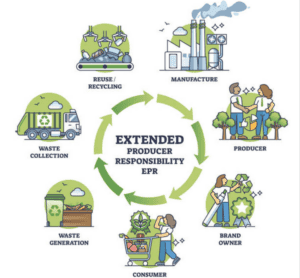
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): EPR policies hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal and recycling. This encourages companies to design electronics that are easier to repair, recycle, or repurpose, and reduces the overall environmental footprint of electronic devices.
- Corporate Sustainability Initiatives: Many tech companies are adopting sustainability goals aimed at reducing e-waste. Apple, for example, has committed to using 100% recycled materials in its products, while Dell runs a global recycling program that recovers e-waste for responsible recycling and reuse.
In Last
The e-waste challenge is a pressing global issue, but it also presents an opportunity to rethink how we interact with technology and the environment. By turning tech trash into opportunity, we can reduce environmental harm, recover valuable resources, create economic growth, and protect human health. Through innovative recycling practices, responsible consumer behavior, and government and corporate responsibility, we can rise to meet the e-waste challenge and work toward a more sustainable and equitable future.