This technological boom, while beneficial for the economy, has led to a significant increase in electronic waste (e-waste). E-waste comprises discarded electronic devices and components, including computers, smartphones, televisions, and other gadgets. This article delves into the challenges and solutions related to e-waste management in Bangalore.
The Growing E-Waste Problem
Bangalore’s rapid technological advancement and increasing consumerism have led to a surge in e-waste generation. According to various studies, India generates millions of tons of e-waste annually, and Bangalore contributes significantly to this figure through e waste management in Bangalore. The key contributors to e-waste in Bangalore include:
- Consumer Electronics: Smartphones, laptops, tablets, and other personal electronic devices are frequently upgraded, leading to a high turnover of old devices.
- Industrial Electronics: The city’s vast IT and manufacturing sectors generate substantial amounts of obsolete industrial equipment.
- Household Appliances: With rising disposable incomes, households are increasingly discarding old appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and microwaves.
Environmental and Health Impacts of E-Waste
Improper disposal of e-waste can have severe environmental and health repercussions:
- Toxic Substances: E-waste contains hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, cadmium, and brominated flame retardants. When improperly handled, these substances can leach into the soil and groundwater, causing contamination.
- Air Pollution: Burning e-waste to extract valuable metals releases toxic fumes into the air, contributing to air pollution and respiratory problems.
- Health Hazards: Exposure to toxic chemicals from e-waste can lead to various health issues, including neurological damage, kidney problems, and developmental disorders.
Current E-Waste Management Practices
Ewaste in Bangalore involves several stakeholders, including the government, private companies, and informal sectors. The current practices include:
- Formal Recycling Units: Several authorized e-waste recycling facilities in Bangalore adhere to environmental regulations and ensure the safe disposal of electronic waste.
- Informal Sector: A significant portion of e-waste is handled by the informal sector, which often employs unsafe methods to dismantle and recycle e-waste, leading to environmental pollution and health risks.
- Corporate Initiatives: Many IT companies in Bangalore have initiated e-waste management programs as part of their corporate social responsibility (CSR) efforts. These programs often include take-back schemes and partnerships with certified recyclers.
- Government Regulations: The Indian government has implemented the E-Waste Management Rules, which mandate proper disposal and recycling of e-waste. These rules place the responsibility on producers to collect and recycle e-waste.
Challenges in E-Waste Management
Despite the efforts, several challenges hinder effective e-waste management in Bangalore:
- Lack of Awareness: Many consumers are unaware of the environmental and health impacts of e-waste and the importance of proper disposal.
- Informal Sector Dominance: The informal sector’s unsafe recycling practices continue to dominate the e-waste management landscape.
- Inefficient Collection Systems: There is a lack of efficient and accessible collection systems for e-waste, leading to improper disposal by consumers.
- Regulatory Gaps: While regulations exist, enforcement and compliance remain weak, allowing illegal e-waste handling practices to persist in ewaste recycling Bangalore.
- Limited Recycling Capacity: The formal recycling infrastructure is often insufficient to handle the growing volume of e-waste.
Solutions and Strategies for Effective E-Waste Management
To address the challenges and improve e-waste management in Bangalore, a multi-faceted approach involving various stakeholders is essential.
Here are some possible resolutions and plans:
- Raising Awareness:
- Educational Campaigns: Conduct awareness campaigns in schools, colleges, and communities to educate people about the dangers of e-waste and the importance of proper disposal.
- Corporate Initiatives: Companies can play a crucial role in educating their employees and customers about e-waste management through workshops, newsletters, and social media campaigns.
- Strengthening Regulations and Enforcement:
- Strict Enforcement: Ensuring strict enforcement of existing e-waste management regulations and penalizing non-compliance.
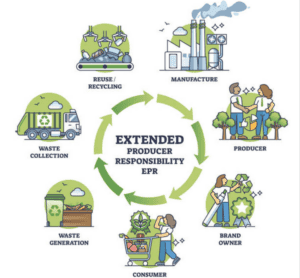
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Strengthening EPR policies to hold producers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including take-back and recycling.
- Improving Collection Systems:
- Accessible Collection Points: Establishing more e-waste collection points across the city to make it easier for consumers to dispose of their electronic waste responsibly.
- Door-to-Door Collection: Implementing door-to-door e-waste collection services, especially in residential areas, to increase collection rates.
- Supporting the Formal Sector:
- Incentives and Subsidies: Providing financial incentives and subsidies to formal recycling units to enhance their capacity and efficiency.
- Partnerships: Encouraging partnerships between formal recyclers and the informal sector to improve recycling practices and ensure safe disposal of e-waste.
- Promoting Recycling and Reuse:
- Repair and Refurbishment: Encouraging the repair and refurbishment of electronic devices to extend their lifespan and reduce e-waste generation.
- Second-Hand Markets: Supporting the growth of second-hand electronics markets to promote the reuse of devices.
- Technological Innovations:
- Advanced Recycling Technologies: Investing in advanced recycling technologies that can efficiently and safely process e-waste by ewaste recycling facility Bangalore.
- Research and Development: Supporting research and development initiatives focused on sustainable e-waste management practices.
In Conclusion
Effective e-waste management is crucial for safeguarding the environment and public health in Bangalore. As the city continues to grow as a technology hub, the volume of e-waste will inevitably increase. Addressing this issue requires a collaborative effort involving government authorities, businesses, and the community. By raising awareness, strengthening regulations, improving collection systems, supporting the formal recycling sector, promoting recycling and reuse, and leveraging technological innovations, Bangalore can pave the way for a sustainable future. Proper e-waste management not only helps in mitigating environmental pollution but also contributes to the conservation of valuable resources and the creation of green jobs.